12 KiB
WINDOWS_INSTALL
This is an installation guide for Windows, covering all the steps needed to begin developing code for the Urban Simulation Platform 'Hub'. At the end of this process you will have installed and configured all the necessary applications, set up your own project on CERC's Gitlab and created your first python file.
Prepare your environment
g To develop any new code for the Urban Simulation Platform you must have the right software applications installed and configured. The Platform is written in python and so the applications you need are:
- Miniconda
- Python Editor
You also need to register a user account with the CERC's code repository on Gitlab and have the necessary permissions for creating new code. For that purpose, please, contact Guillermo (guillermo.gutierrezmorote@concordia.ca) or Koa (kekoa.wells@concordia.ca) as soon as possible.
Get Miniconda
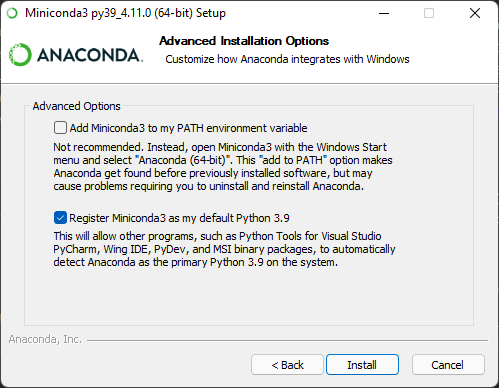
- Download Miniconda for Windows for Python version 3.9.
- Run the installer and select in the corresponding window Register Miniconda3 as my default Python 3.9.
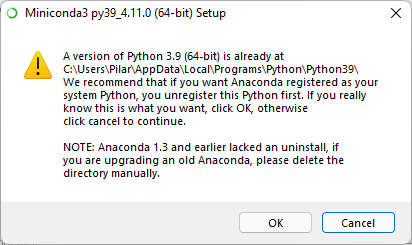
If you already installed a Python interpreter, the following message will warn you:
Click OK and then, click Install.
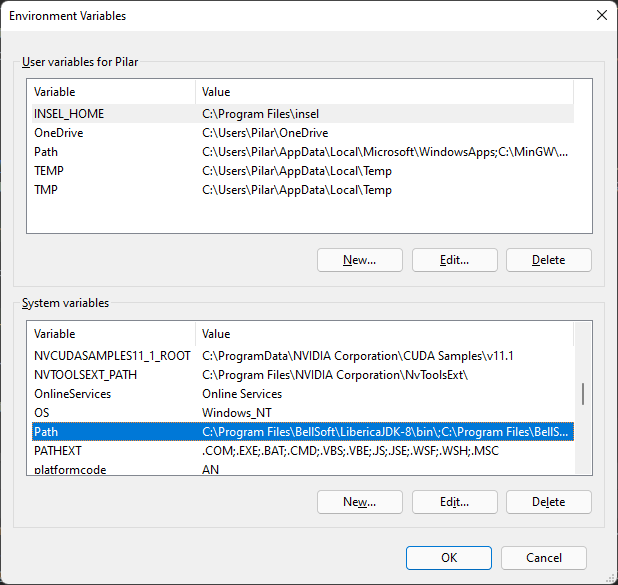
Once you are done, add Miniconda to the Path by clicking on New and writing the path where conda.exe was installed.:
Now, restart the computer to update the Path.
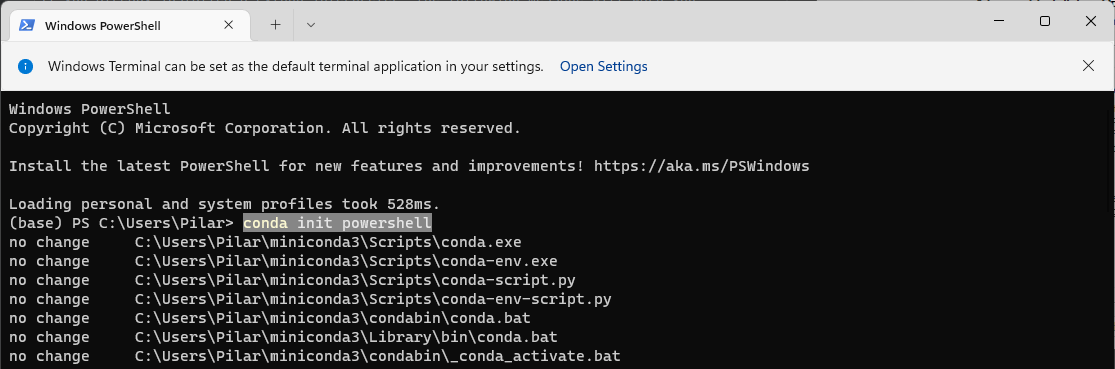
Finally, open a terminal and type 'conda init powershell'.
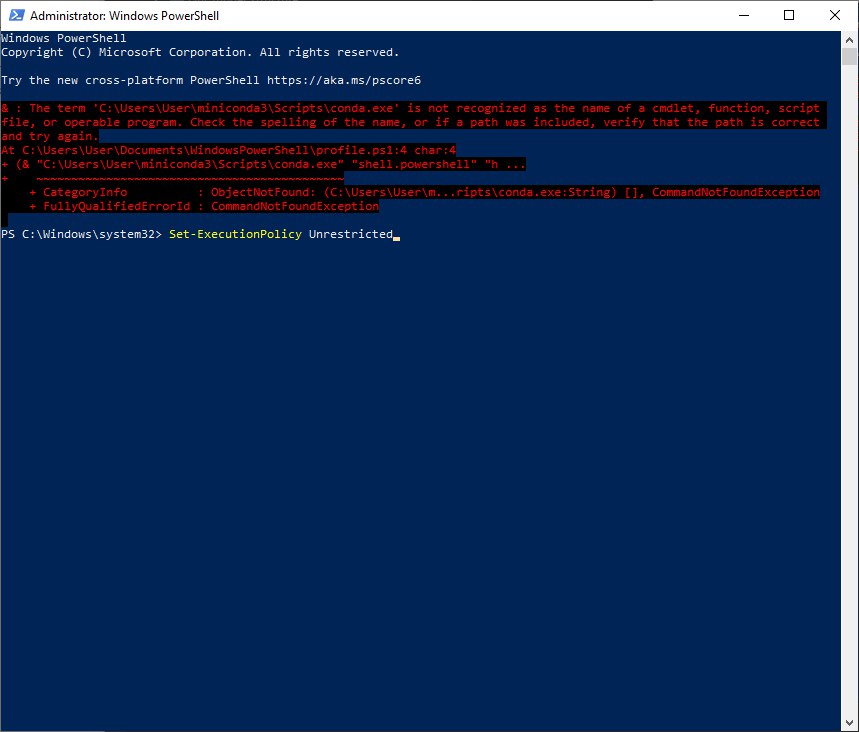
NOTE: This final step could produce the following error: The term '...' is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet, function,...
To solve it, type 'Set-ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted' as shown in the image.
Get a Python editor
- You will need a python editor in order to import the existing Hub source code and to write your own python code. Whilst this is a personal choice we would like to recommend PyCharm Community Edition, an excellent open-source python editor.
- Run the installer, and follow the installation instructions for PyCharm, you may change a few options, but the default ones should be fine.
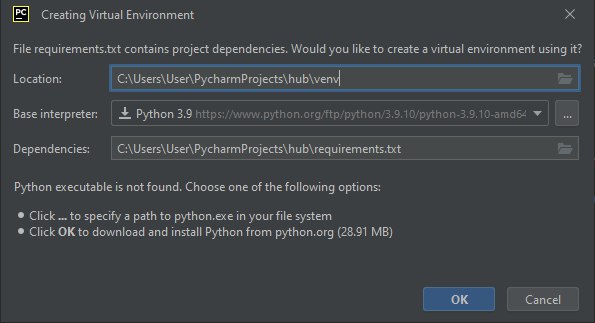
NOTE: If Pycharm asks you to create a Virtual Environment, click Cancel. You will do it later using Conda instead.
Get the CERC Hub source code
- Run PyCharmCE
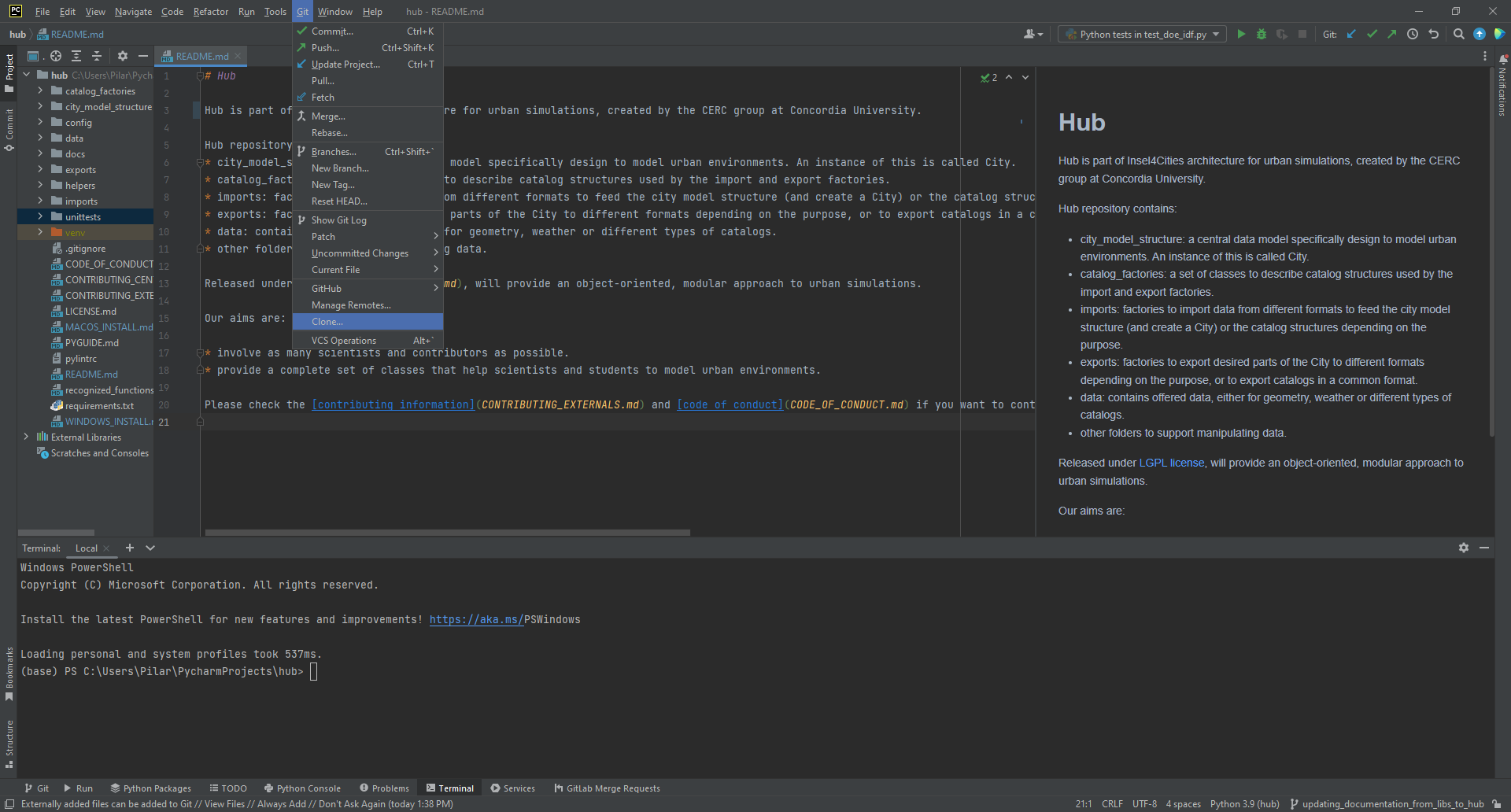
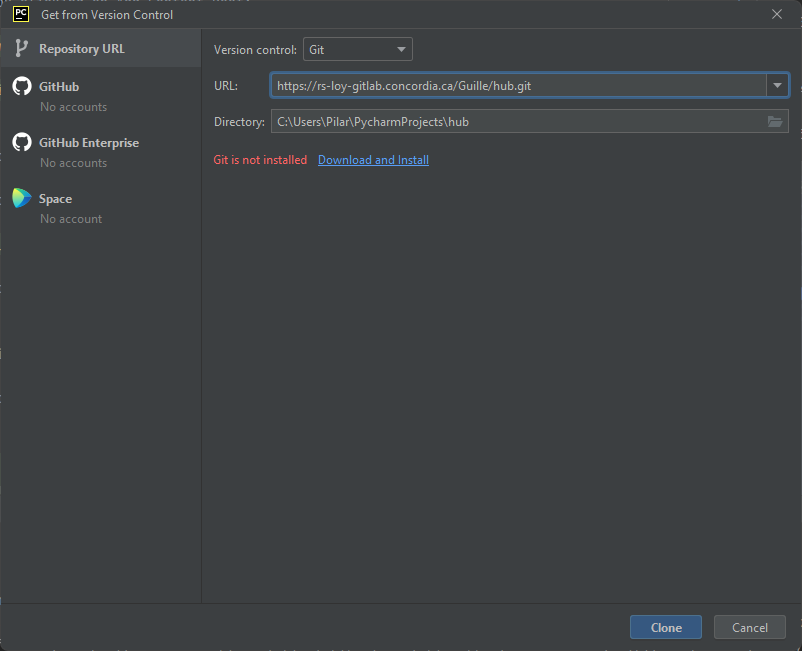
- Click on the Get from VCS button in the top right of the window.
You can find it also at Git->Clone...
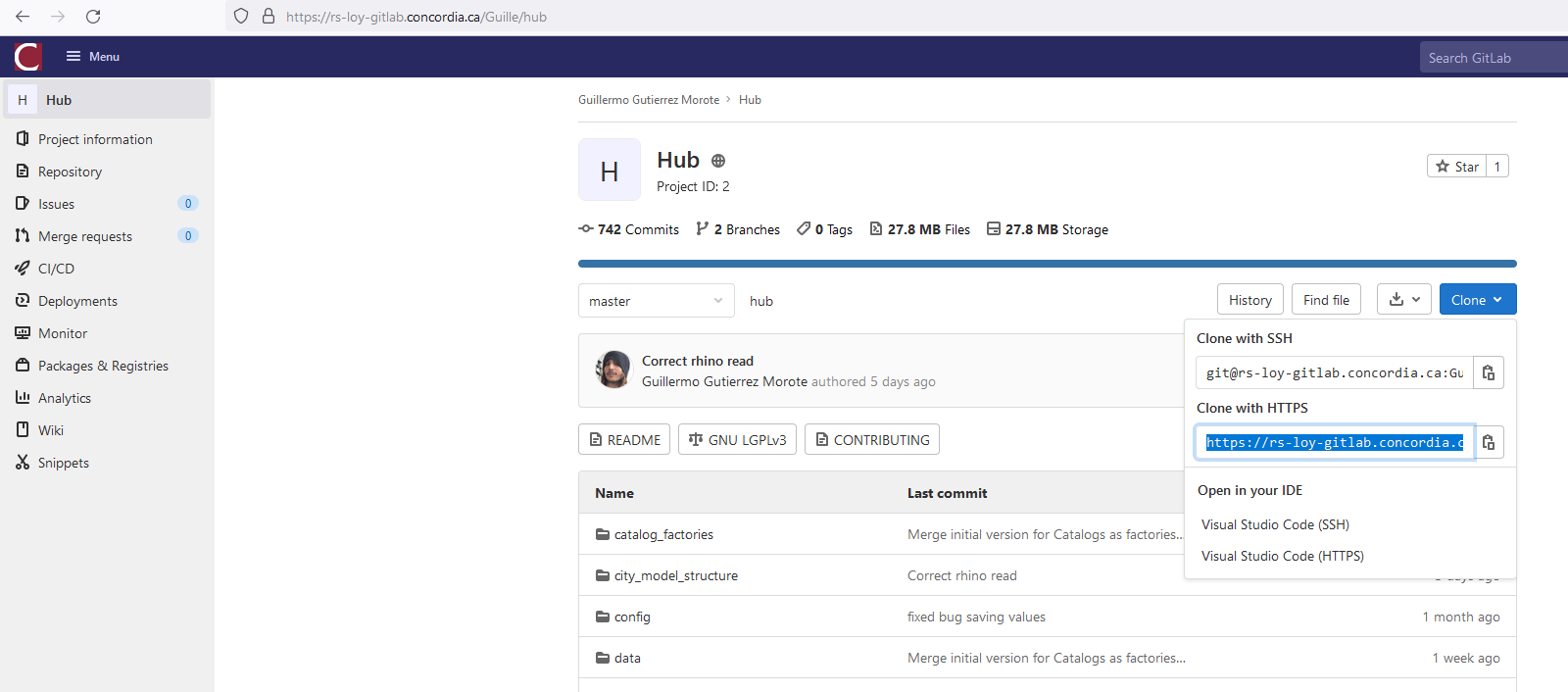
- Select Git as the Version control. For the URL use the link to the Hub repository, as seen below.
(You can also copy this URL by going to the Hub repository in Gitlab and clicking on the Copy URL button, next to Clone with HTTPS)
The Directory to store the Hub source code locally is automatically created for you. Edit this if you prefer it to be stored somewhere else.
Note: If you see a message saying Git is not installed, click on the Download and install and follow instructions.
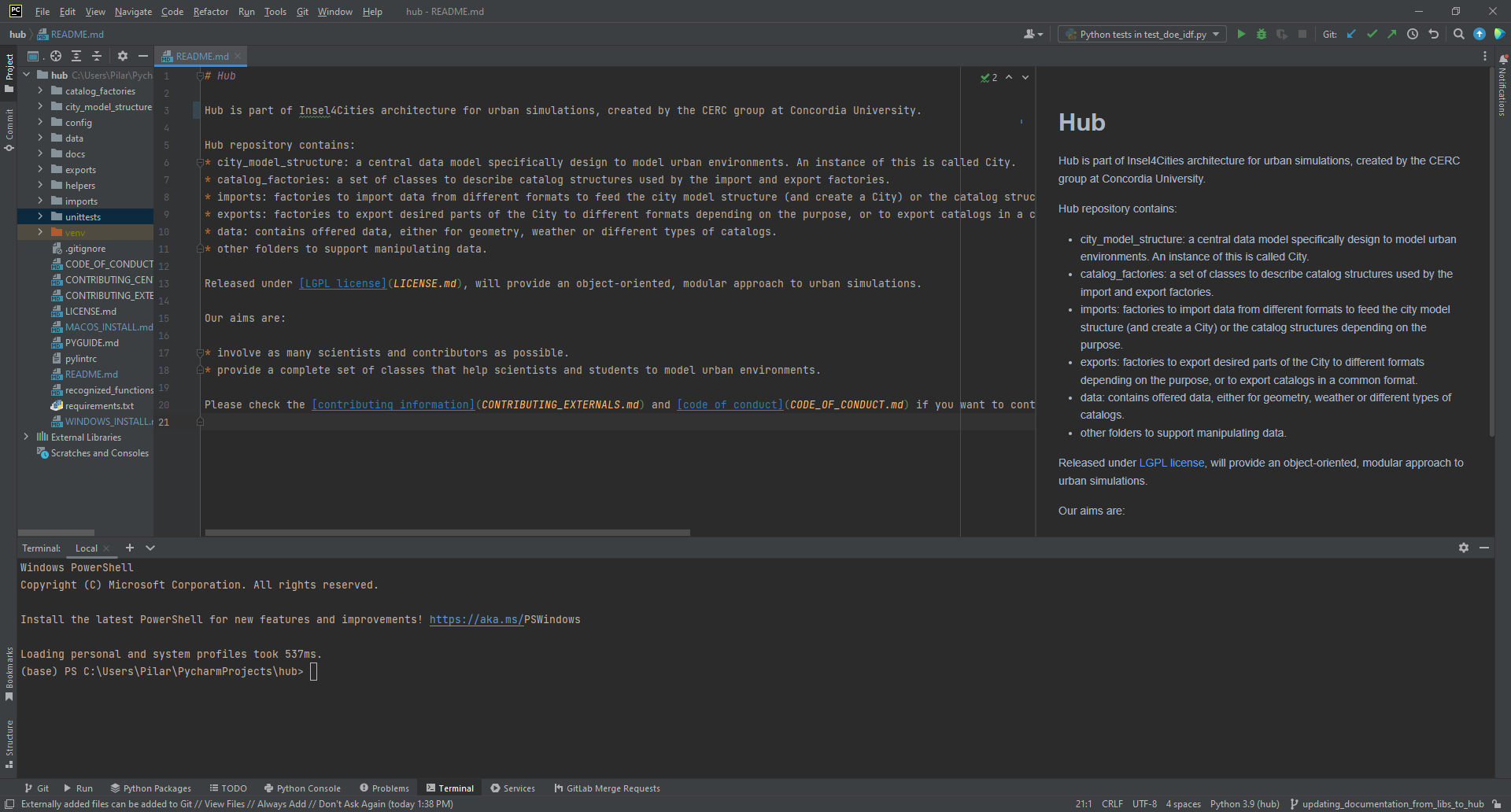
- Click the Clone button to download CERC hub source code. You will then see the project directories and files below, with the hub readme document displayed. You have successfully cloned a copy of the CERC hub onto your computer.
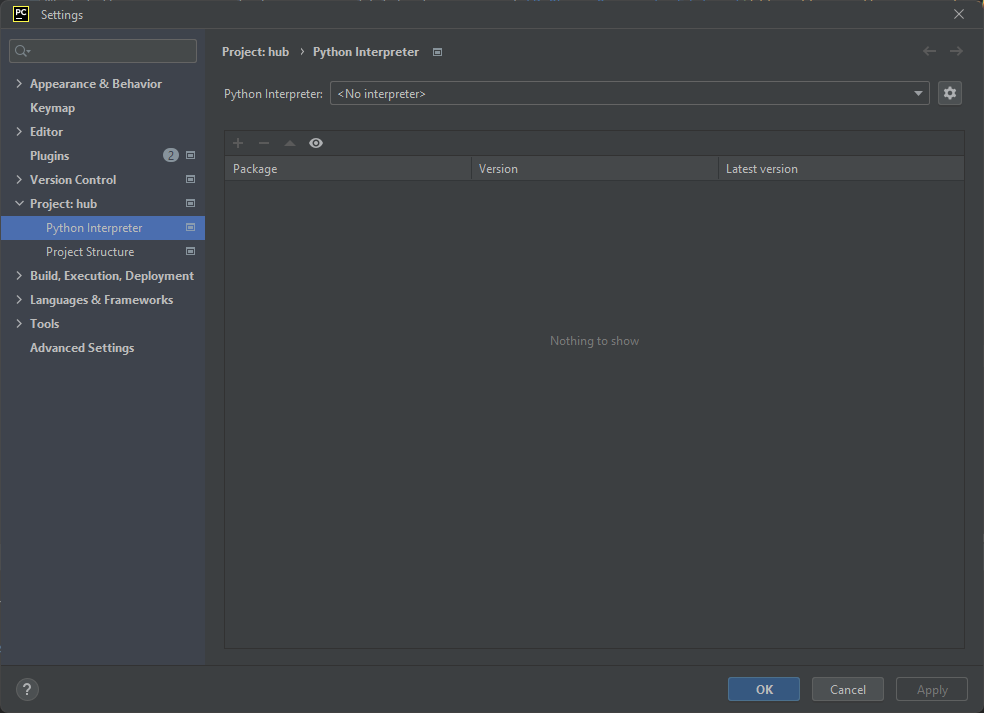
Configure Python Interpreter
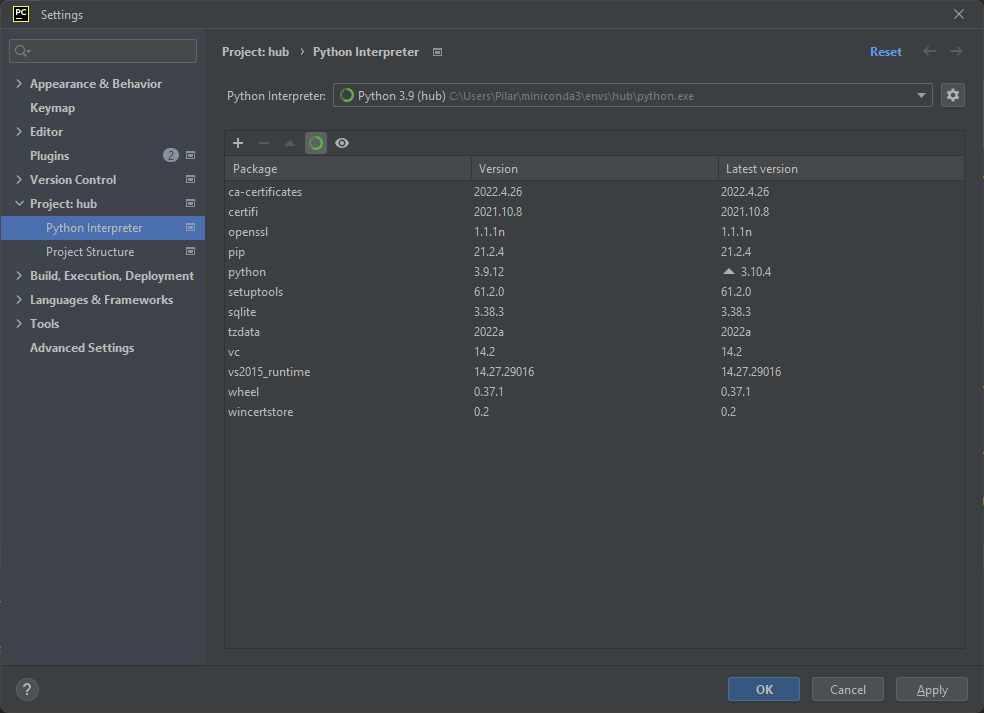
- Click on File, and select Settings... from the drop-down menu. The Settings window will appear. From the panel on the left, select Project: hub->Python Interpreter and you will see the following window:
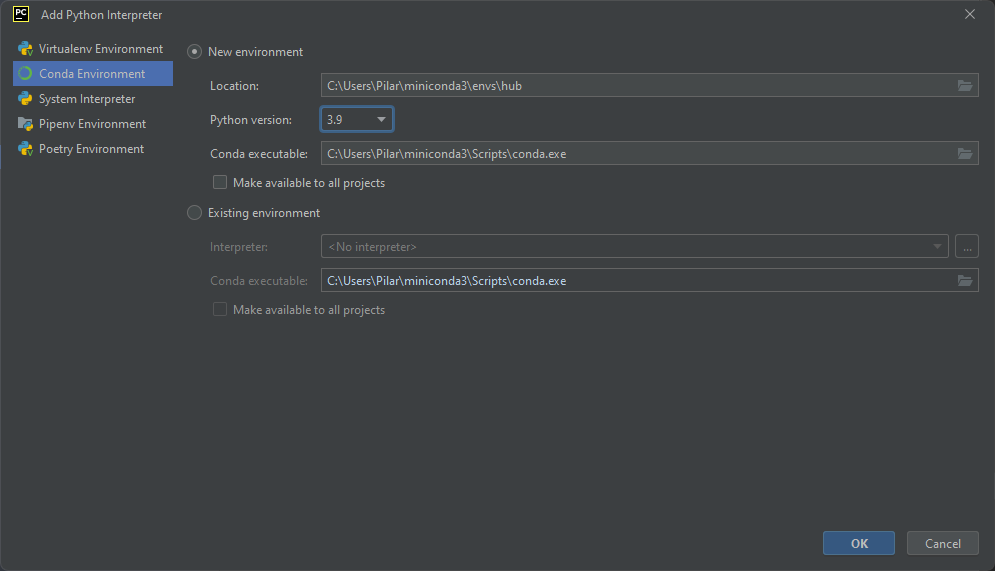
- Click on the little gear on the right and click Add.... In the new window, click on Conda Environment, select New environment and the Python version 3.9.
You should end with the following window:
Click OK to close it.
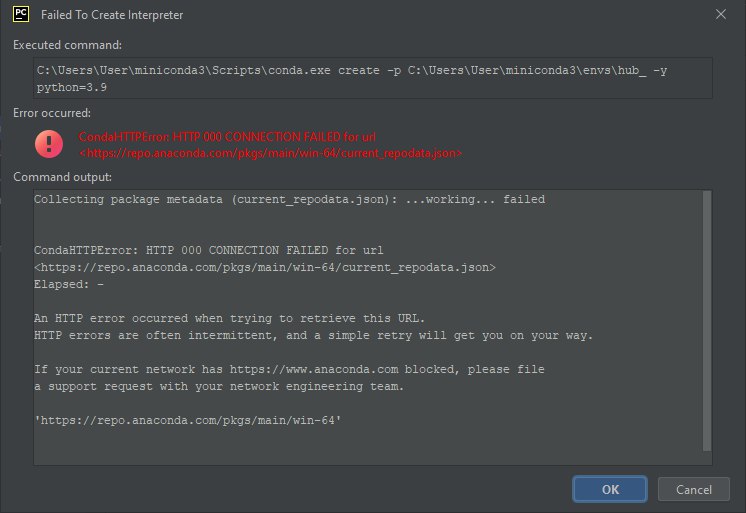
NOTE: This final step could produce the following error:
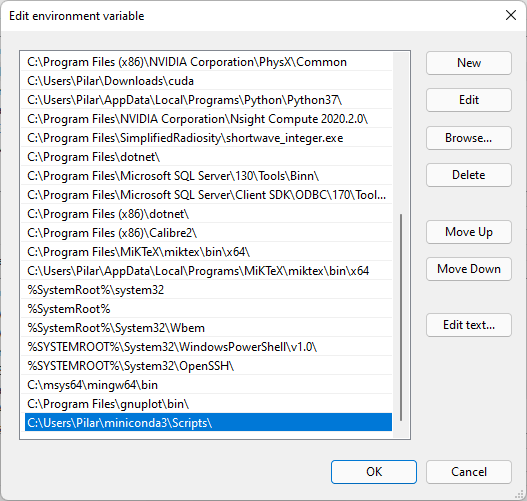
To solve it, add to the Path (as explained in [previous chapter Get Miniconda](WINDOWS_INSTALL.md#Get Miniconda)) the following paths:
- C:\Users\User\miniconda3\Library\bin
- C:\Users\User\miniconda3
- C:\Users\User\miniconda3\Scripts
Restart the computer and come back to step 1 of this section.
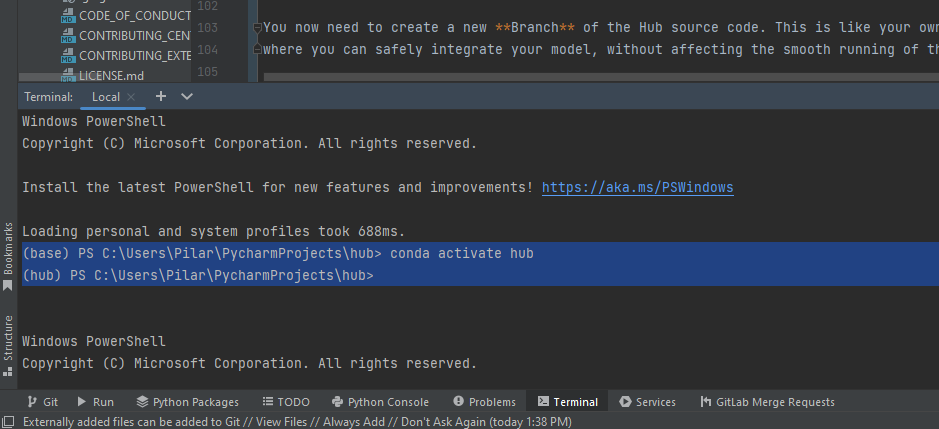
- Go to the Terminal (a tab in the bottom) to finish this process. You should see PS C:\Users\Pilar\PycharmProjects\hub> preceded either by (base) or (hub). If non of those are there, be sure that you have Miniconda installed and included in the path as explained in [previous chapter Get Miniconda](WINDOWS_INSTALL.md#Get Miniconda). If not, do it, restart Pycharm, and come back to this point.
If the environment you are working in is (base), type 'conda activate ' and the project's name, in this case 'conda activate hub'. Click enter, and the environment should change to (hub). If this didn't work, contact Guillermo (guillermo.gutierrezmorote@concordia.ca) or Koa (kekoa.wells@concordia.ca) for some help.
- Once you are in (hub), type 'pip install -r .\requirements.txt' and wait until all requirements are installed. In the bottom-right corner you should be able to see a bar showing the progress.
Create Your Own Branch of the Hub
You now need to create a new Branch of the Hub source code. This is like your own special version of the Hub, where you can safely integrate your model, without affecting the smooth running of the Main Branch Hub and the Platform.
To create your working branch you need rights to edit the project. Please, contact Guillermo (guillermo.gutierrezmorote@concordia.ca) or Koa (kekoa.wells@concordia.ca) to get those rights and then follow the instructions.
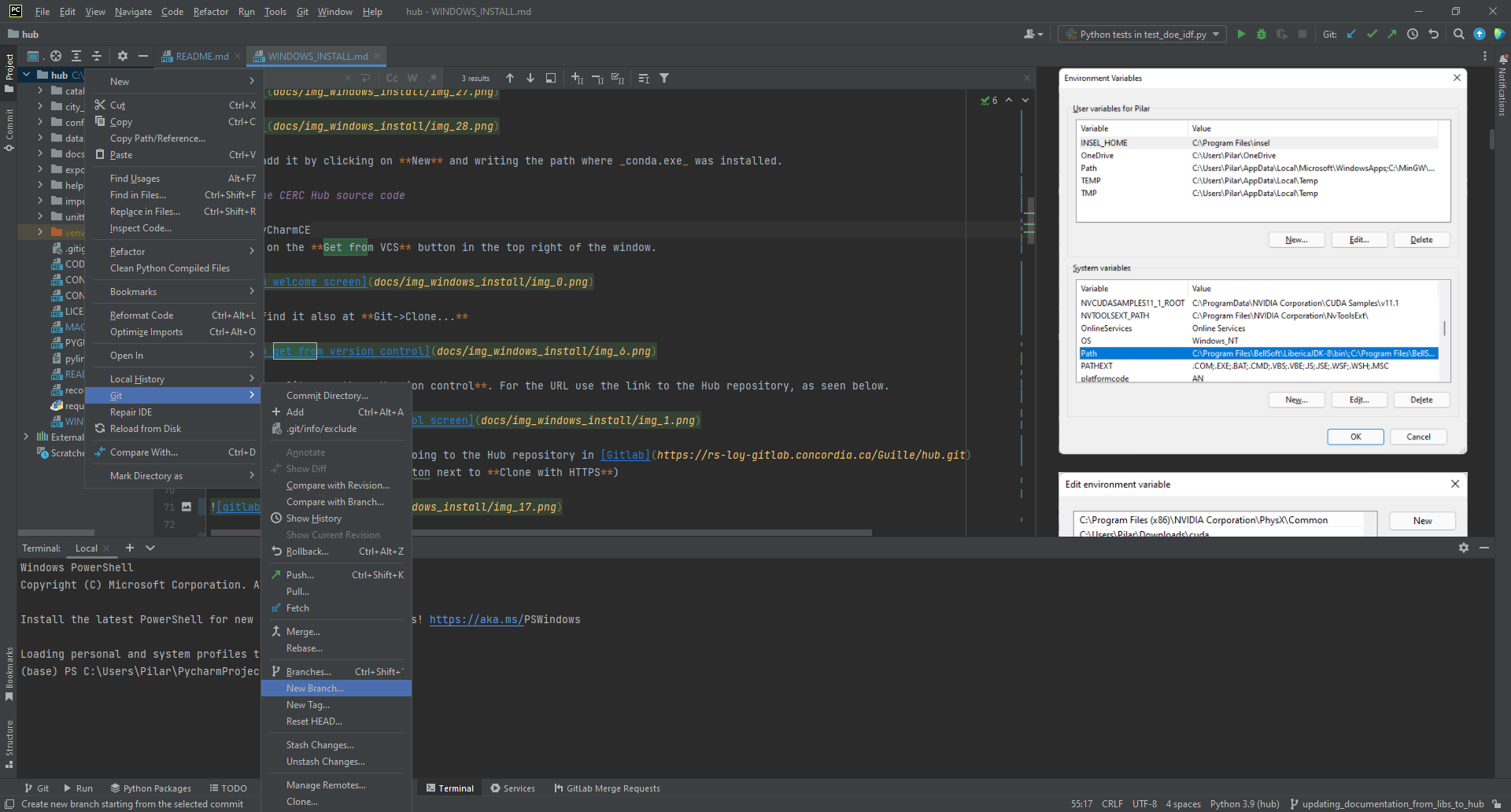
- Create your working branch by right-clicking on the project folder (hub) and then selecting Git->New Branch...
- Give a name to your branch that has some sense of what will be done with it, updating_documentation, lca_classes,... And, click on the Create button.
-
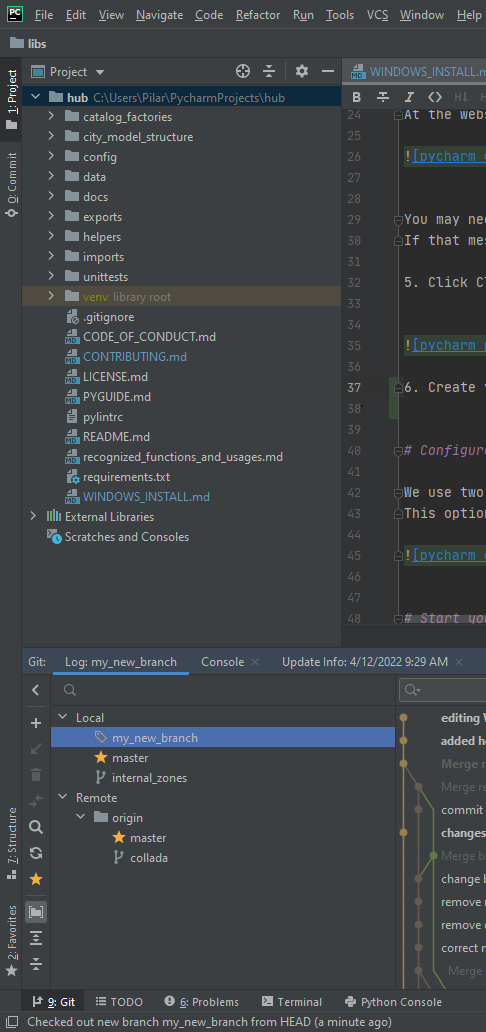
Click on the Git button in the bottom-left corner to pop-up the window showing the Git information. See your new branch has been created under Local.
-
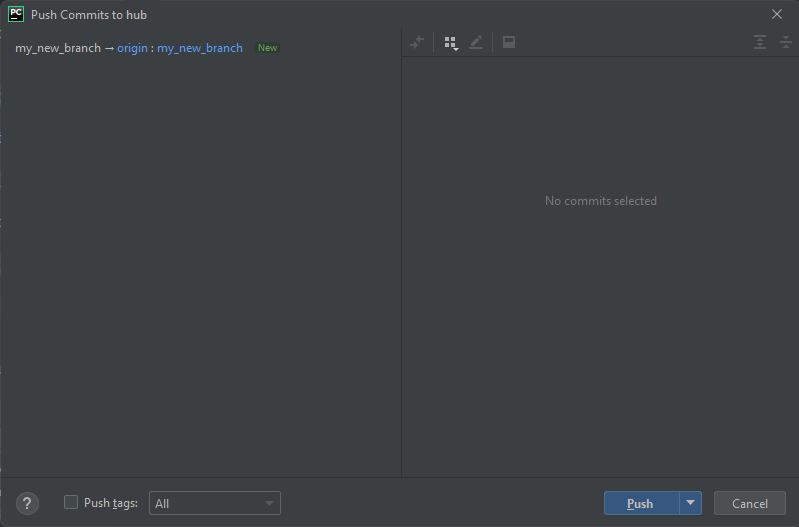
Now we need to let the CERC Gitlab repository know about this new branch. You do this by right-clicking on your branch and selecting Push... from the drop-down menu.
-
Then click on the Push button at the bottom-right of the Push Commits window.
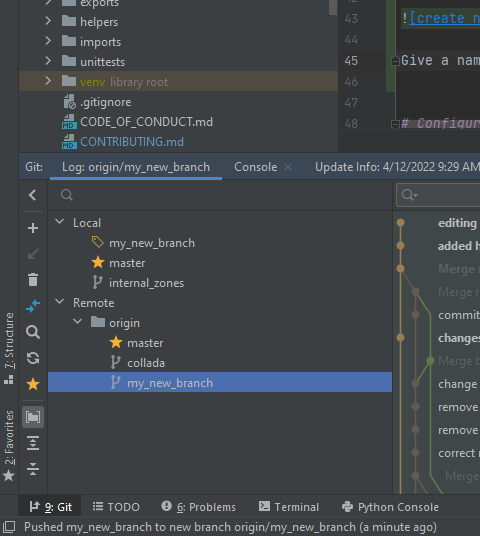
Check that your branch now appears in the Remote branch hierarchy, in the bottom-left corner. If it does not appear, contact Guillermo (guillermo.gutierrezmorote@concordia.ca) or Koa (kekoa.wells@concordia.ca), to find the reason of the error.
If your branch is there, you are done with this part. Now you are all set to contribute to Hub or to use it for your own projects!
Configure Pycharm
When integrating your model with the Platform, it is important that you follow CERC’s coding style guidelines. One of the rules is that we use two spaces as a tab instead of the standard pep8 four spaces indentation. This option can be configured in PyCharm at the settings screen.
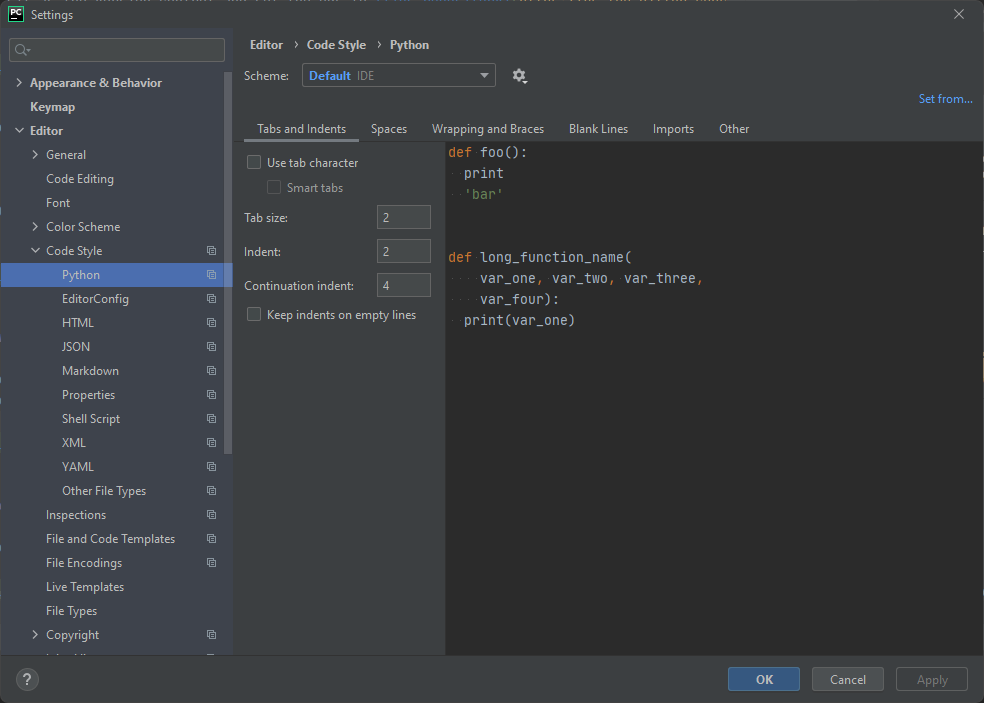
To access the settings screen, click on File, and select Settings... from the drop-down menu. The Settings window will appear. From the panel on the left, select Editor->Code Style->Python and you will see where tab size can be changed. Change it to 2. See the picture below.
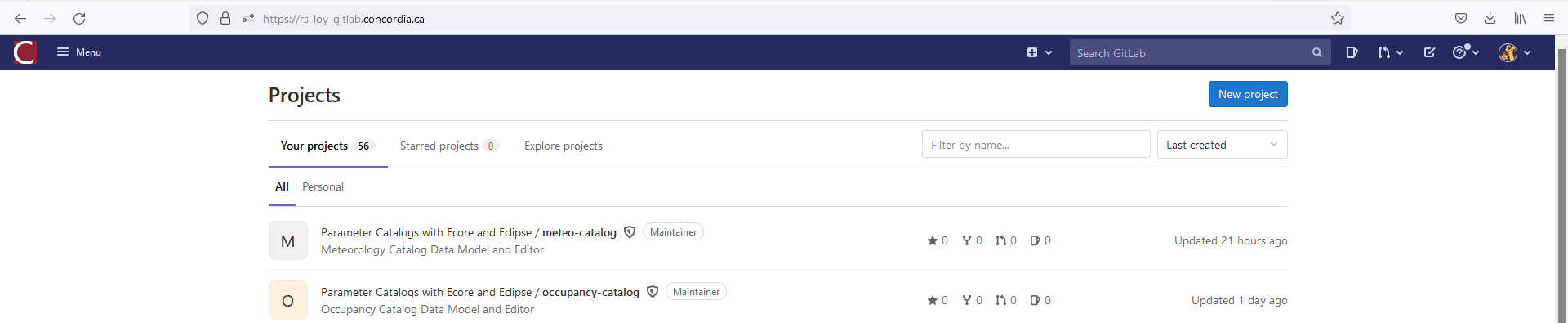
Set up a new project on Gitlab
- Open a browser and to the CERC Git. Click on the blue New project button.
-
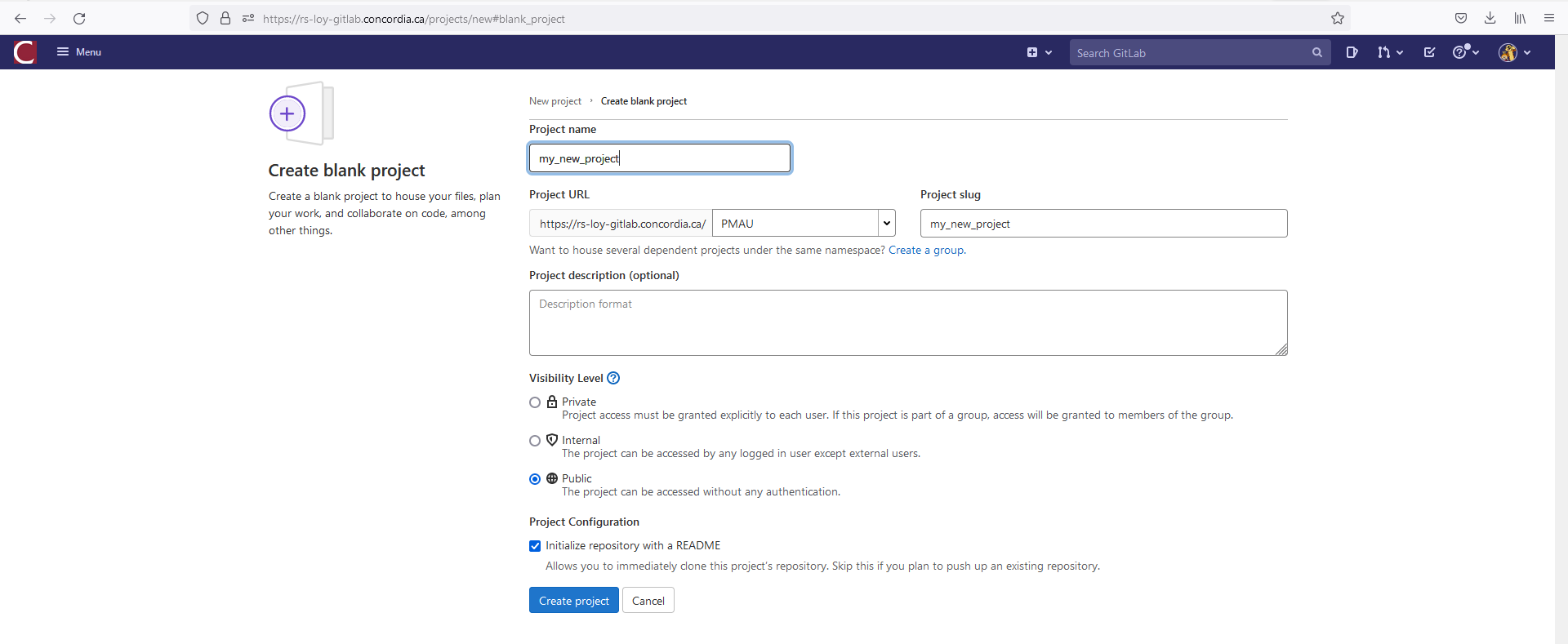
Choose the Create blank project option from the three options seen below.
-
Type in a name that describes your project: hp_workflow, bus_system_optimization... (remember to follow the CERC naming conventions described in the Coding Style). Check the option Initialize repository with a README, and ideally, check the Visibility Level to be Public. Then click on the Create project button.
You should then see a confirmation screen with all the information about your new project.
Get your project into Pycharm
-
Now you can make a clone of this project, within PyCharm. First, copy the URL by clicking on the blue Clone button and then click on the Copy URL button, next to the Clone with HTTPS link.
-
Switch back to PyCharm and close the Hub project by choosing File->Close Project. You will then see the Welcome To PyCharm window again.
-
Clone a copy of your Project into PyCharm, following the steps 2-6 of the GET THE CERC HUB SOURCE CODE section above, but using the URL link that you just copied for your gitlab project.
-
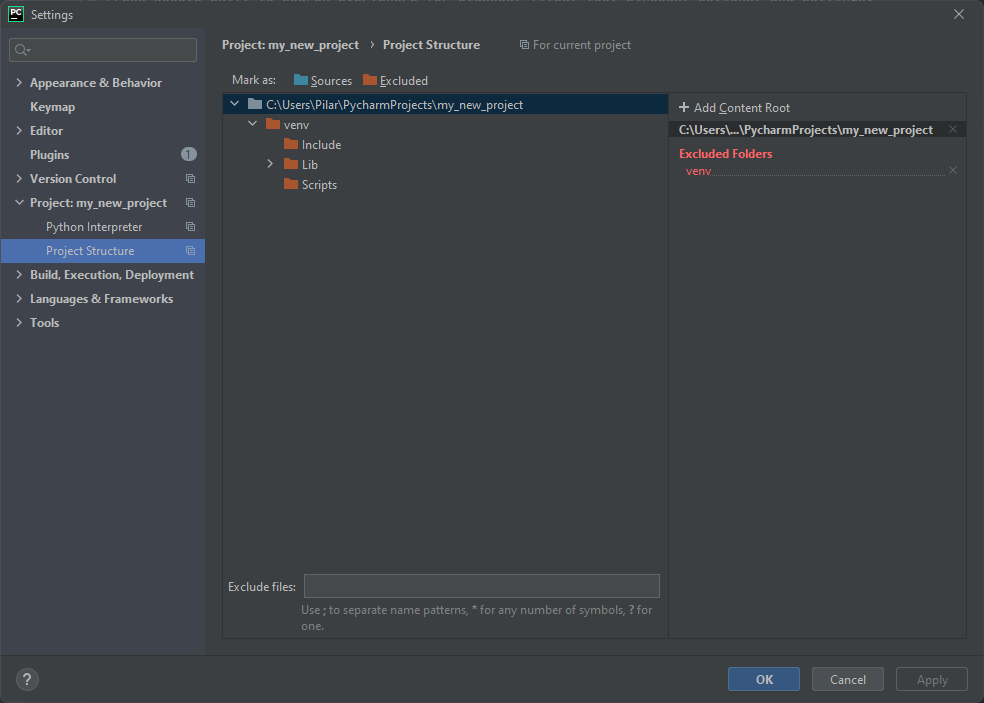
Select File->Settings to open the Settings window. From the panel on the left click on Project: -> Project Structure.
-
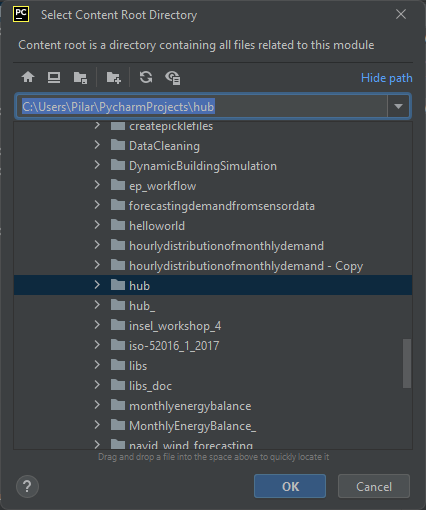
Add the Hub project to your own, by clicking on Add Content Root:
-
Still in the Settings window, configure your Python interpreter (yes, again, you have to do this step for each new project) by following steps 1 to 5 explained in [chapter Configure Python Interpreter](WINDOWS_INSTALL.md#Configure Python Interpreter). Then, to install the requirements, type 'cd..' and enter. Then 'pip install -r .\hub\requirements.txt' and wait until all requirements are installed. In the bottom-right corner you should be able to see a bar showing the progress. Finally, type 'cd ' and your project's name.
-
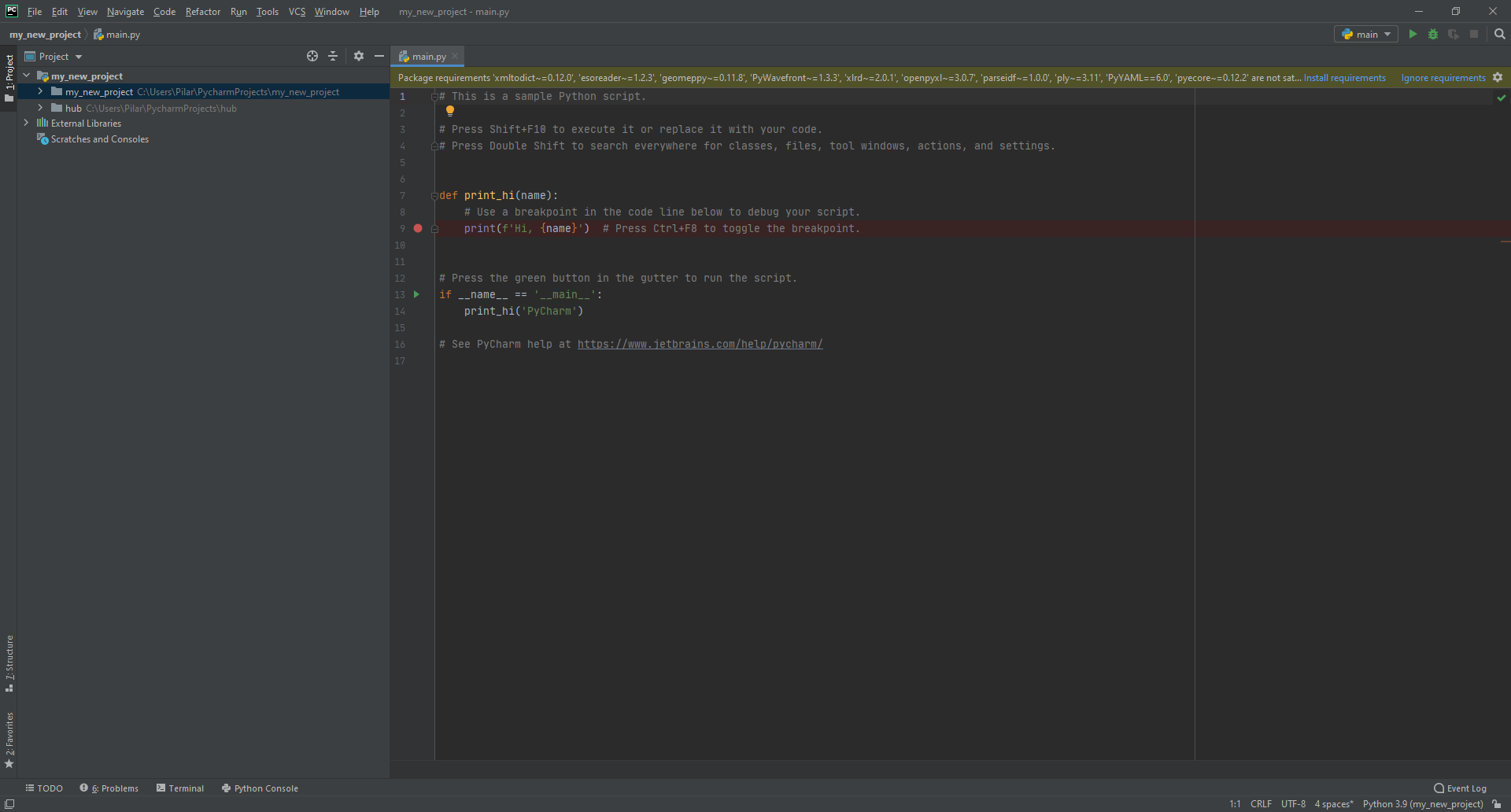
Now, add your first file to your project and click on install requirements to automatically download all the dependencies (in blue at top-right corner).
If the blue message doesn't appear, click on the Terminal tab (bottom-left), type pip install -r .\requirements.txt and press enter.
- When all the dependencies are satisfied, you are all set to start importing your first city model.
Add the following code to your main.py
from imports.geometry_factory import GeometryFactory
city = GeometryFactory('citygml', 'myfile.gml').city
- Always remember to push your own project changes as the last thing you do before ending your working day! First, commit your changes by clicking on the green check in the top-right corner of Pycharm. Add a comment that explains briefly your changes. Then, pull by clicking on the blue arrow to be sure that there are no conflicts between your version (local) and the remote one (gitlab). Once the conflicts are solved and the merge in local is done, push the changes by clicking on the green arrow.